How to improve your gut microbiome health in 16 simple steps

Written by Georgia Chappell & Reviewed by Paul Holmes.
Imagine an internal metropolis teeming with countless residents, surpassing the number of your own cells tenfold and dwarfing your genetic repertoire a hundred times over. This vibrant ecosystem is known as your gut microbiome—composed of an array of bacteria residing within your digestive tract. These organisms are collectively termed gut microbes.
Your body relies on this complex assembly, the gut microbiota—which boasts in excess of 1000 distinct microbial species—to perform essential tasks ranging from metabolic processes and nutrient absorption to maintaining physiological balance and bolstering immune defences.
The inception of this microbe-filled city takes place at birth, where it’s shaped by various determinants such as delivery method, maternal vaginal flora, surrounding environment for the infant, and subsequent nourishment.
Eventually reaching stability among broader classifications known as phyla while retaining considerable diversity at finer taxonomic levels (species), this rich variation plays a pivotal role in enabling the myriad of functions executed by the human gut microbiota itself. Among these roles are breaking down indigestible carbohydrates into usable components, synthesising vital vitamins and amino acids that our bodies need to thrive, along with mounting safeguards against invading pathogens.
Why is gut microbiome health crucial, and how do you improve gut microbiome naturally? With a direct impact on immunity, digestion, and even mental well-being, nurturing your microbiome is incredibly beneficial.
In this no-nonsense guide, you’ll discover 16 practical ways to enhance your gut health with natural, attainable changes. Expect to finish this article with the knowledge to take proactive steps toward a healthier you.
Key Takaways
- A diverse diet rich in plants, legumes, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and fermented foods is key to a healthy gut microbiome.
- Lifestyle factors such as regular exercise, stress management, good sleep hygiene, staying hydrated, and mindful eating habits have a significant impact on gut health.
- Personalised guidance from healthcare professionals, cautious use of antibiotics, and mindful selection of pre- and probiotic supplements contribute to maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
What is your Gut microbiome?
Imagine an internal metropolis teeming with countless residents, surpassing the number of your own cells tenfold and dwarfing your genetic repertoire a hundred times over. This vibrant ecosystem is known as your gut microbiome—composed of an array of bacteria residing within your digestive tract. These organisms are collectively termed gut microbes.
Your body relies on this complex assembly, the gut microbiota—which boasts in excess of 1000 distinct microbial species—to perform essential tasks ranging from metabolic processes and nutrient absorption to maintaining physiological balance and bolstering immune defences.
The inception of this microbe-filled city takes place at birth, where it’s shaped by various determinants such as delivery method, maternal vaginal flora, surrounding environment for the infant, and subsequent nourishment.
Eventually reaching stability among broader classifications known as phyla while retaining considerable diversity at finer taxonomic levels (species), this rich variation plays a pivotal role in enabling the myriad of functions executed by the human gut microbiota itself. Among these roles are breaking down indigestible carbohydrates into usable components, synthesising vital vitamins and amino acids that our bodies need to thrive, along with mounting safeguards against invading pathogens.

How Does Your Gut Microbiome Impact Your Overall Health?
How does the bustling ecosystem of your gut microbiome impact your well-being, you might wonder? Imagine a healthy gut microbiome as a metropolis functioning at its prime. In such harmonious conditions, just like an efficient city, your digestive tract flourishes. The equilibrium within your gut flora is pivotal for moulding the immune system and safeguarding against exaggerated responses to harmless substances. This balance has implications on neurological functions and stress response through the communication pathways known as the gut-brain axis.
When there’s disruption in this delicate balance, it’s akin to urban disarray – chaos ensues with detrimental effects on human health. An unbalanced population of gut bacteria can pave the way for various ailments from digestive issues like IBS and IBD to systemic disorders including obesity and type 2 diabetes. Even one’s mental health isn’t spared from potential repercussions resulting in mood-related conditions such as anxiety or depression. Thus keeping a balanced intestinal microenvironment remains essential not only for nurturing a resilient immune system but also for sustaining overall bodily health.
16 steps on how to improve your gut microbiome
How can you promote the flourishing of your gut city? Fortunately, enhancing your gut health isn’t about taking extreme steps. It involves integrating minor, manageable adjustments into your eating habits and way of living. To aid in this endeavour, we’ve compiled an extensive guide that outlines 16 natural methods for elevating your gut health. Now let’s get started!
1. Food variety is the key
Just as this city thrives on assorted resources and roles for optimal operation, so too does your healthy gut require varied dietary inputs to sustain its well-being. By incorporating at least 30 distinct types of plant foods each week—encompassing grains, legumes like (beans and lentils) nuts, seeds, herbs and spices, to fruits and vegetables, you can markedly enhance both the variety and vitality of your gut’s microbial inhabitants.
Such a nutritional strategy ensures that you deliver ample prebiotic nourishment needed by the beneficial bacteria populating your healthy gut. Imagine it as hosting an elaborate feast for these microscopic denizens. Every individual plant food offers sustenance to specific groups of beneficial microbes. This not only bolsters their numbers, but also fortifies the overall resilience and diversity within the complex ecosystem that is your gut microbiome.

2. Add legumes to your diet
Moving on, let’s discuss the champions of gut health – legumes. These nutrient-dense powerhouses are loaded with protein, complex carbs, fibre, vitamins and minerals making them an excellent dietary selection for maintaining a healthy gut. The abundance of fibre in beans not only increases stool bulk but also serves as nourishment for the beneficial bacteria residing within our digestive tract, thus ensuring efficient operation of our digestion. Henceforth, whether it’s through soups or salads to spreads and even meat substitutes, there are a multitude of options to weave legumes into your meals and provide substantial support to your gut health!
3. Eat more fruits and vegetables
Incorporating a diverse array of fruits and vegetables into your diet is much like cultivating a vibrant garden within the ecosystem of your gut. These foods, brimming with fibres, act as nourishment for the beneficial bacteria residing in your gastrointestinal tract. Embracing a rainbow-like assortment of produce can lead to an enriched and varied gut microbiome, which is pivotal for maintaining optimal gut health.
Delve into the wide selection offered by nature’s bounty: from members of the brassica family such as Brussels sprouts, broccoli, kale, arugula and cabbage to those belonging to the allium group including garlic, onions, shallots, and scallions. The options are indeed plentiful and let us not overlook fermented favourites alongside other fruit selections that include bananas, figs, apples, apricots, and Kiwis. Creating this spectrum on your plate feeds more than just you, it sustains a thriving community within, tailored towards holistic well-being.
4. Choose wholegrains
Consider whole grains as the robust architecture that provides strength and form within your gut metropolis, playing a vital role in fostering a healthier gut microbiome. These grains are replete with dietary fibres which, when fermented by the gut microbiota, result in the generation of health-promoting short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Among these whole grains you’ll find:
- Brown rice
- Quinoa
- Oats
- Barley
- Whole wheat
- Rye
By integrating these nutrient-dense whole grains into your meals, you can support a rich and flourishing community of microbes in your gut.
Therefore, when navigating grocery aisles, reach for items such as brown rice, pasta or oatmeal bread labelled with “whole grain”. Choosing these foods over refined alternatives consistently contributes to microbial diversity and is key to thanking your digestive system!
5. Drink coffee
Let’s delve into the vibrant cafes within your body’s intestinal microbiome metropolis. That’s correct – consuming coffee is associated with an increase in gut microbiome diversity, which in turn enhances general health.
Feel free to enjoy your morning brew with the understanding that it benefits the well-being of your gut.
6. Eat nuts and seeds
Nuts and seeds are the powerhouse nourishment for your intestinal metropolis. They come loaded with fibrous content, polyphenols, and beneficial fats that bolster the diversity of your gut microbiome as well as enhance general wellness.
Hence, incorporating a dash of nuts and seeds into your daily meals is advisable – it’s like giving an energy boost to your gut!
7. Fermented Foods for a Healthy Gut
Consider fermented foods to be akin to the waste management centres within the metropolis of your gut. Laden with probiotics, these foods thrive on prebiotics, fostering a flourishing population of advantageous gut bacteria. Introducing foods high in probiotics into your dietary regime can facilitate a favourable transformation of your gut microbiome, thereby improving the well-being of your digestive system. Probiotic-dense edibles include items like yoghurt, kefir, kombucha, sauerkraut, kimchi, tempeh and miso.

8. Reducing Sugar and Processed Foods
Similarly to how a city must efficiently deal with its waste, your internal ‘gut city’ should also minimise waste by avoiding processed foods, sugary treats, high-fat items, and artificial sweeteners. Consuming these can foster the growth of ‘bad’ gut bacteria and contribute to an unhealthy gut environment. By limiting these harmful food choices, you can support the well-being of your gut ecosystem and decrease the likelihood of health complications associated with poor gut health.
9. Improve your Sleep
Similarly to how a city requires periods of rest, your gut also needs proper downtime. Maintaining good sleep habits is essential for fostering a varied and thriving healthy gut microbiome. Inconsistent sleeping schedules can adversely impact both the variety and equilibrium of the good bacteria already in your gut, thus it’s vital to ensure adequate sleep.

10. Regular Exercise
Just like city parks serve as centres for renewal and development within a city, exercise plays a similar role for your gut – fostering vitality and expansion. Engaging in consistent exercise can favourably alter the makeup and variety of organisms within your gut microbiome.
It doesn’t matter if you prefer a vigorous jog or an intense training session. Ensure that habitual physical activity is part of your daily regimen to maintain a very healthy body and gut.
11. Managing Stress
Similarly to how a city requires an effective plan for handling stress to operate effectively, your gut needs the same. Persistent stress can have adverse effects on the composition of your gut microbiome, causing a disruption in the balance of gut bacteria that is linked with numerous health complications, among them issues related to mental health.
Hence, it’s important to pause and engage in activities that reduce stress for maintaining a healthier condition within your gut bacteria population.

12. The Role of Hydration
Maintaining a well-hydrated system is akin to providing a metropolis with an adequate water supply – it’s fundamentally vital. As a critical element of the human body, water plays several key roles essential for overall health and:
- Facilitating digestion
- Expelling waste from the body
- Regulating internal temperature
- Acting as a lubricant for joints
- Delivering nutrients and oxygen throughout the body’s cells
- Assisting in cellular waste removal
About 50% to 60% of an adult’s total body weight can be attributed to water content. It’s important to ensure you drink enough fluids consistently to support gut health.
13. Mindful Eating Habits
Mindful eating serves gut health in the same way mindful living nurtures a city, creating equilibrium and stability.
By encouraging habits of slow and deliberate mastication, mindful eating contributes to improved digestion and optimal nutrient uptake, thereby enhancing both gut health and overall digestive wellness.

14. Prebiotics and Probiotics Supplements
Ingesting prebiotic and probiotic foods or supplements can lead to a favourable transformation of the human gut and microbiome by fostering the proliferation of beneficial bacteria, much like how infrastructure and amenities improve the operational capacity of a city.
Understanding Prebiotics
Grasping the intricacies of a city’s foundational systems is crucial for its governance, much like comprehending prebiotics is essential for maintaining good gut health. Often dubbed as ‘microbiome fertilisers,’ these prebiotics serve to promote both the proliferation and metabolic vigour of your gut’s beneficial bacteria.
It’s important to ensure that your dietary regimen incorporates foods abundant in prebiotics, which will nourish the advantageous bacterial inhabitants of your gut.
Finding the Right Probiotic Supplement
Similarly to how selecting suitable amenities can improve the quality of life in a city, choosing appropriate probiotic supplements can positively affect your gut health. It’s crucial to make an informed decision because various strains of probiotics yield different health results. You should seek advice from a healthcare provider to identify the correct supplement tailored to your unique needs and any existing health issues.
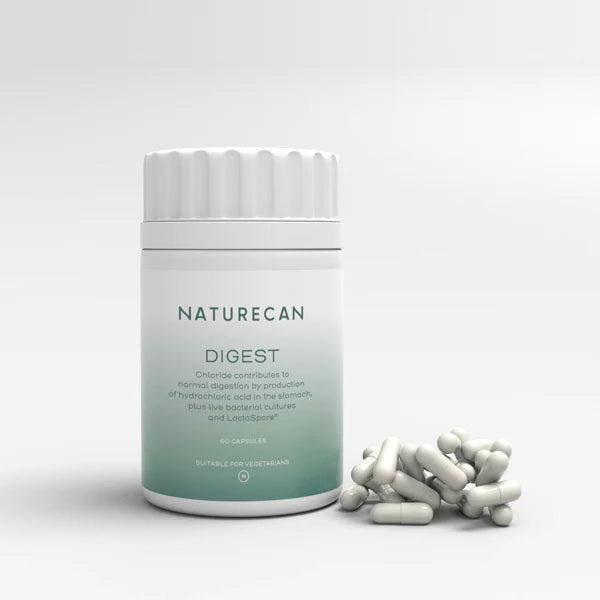
Introducing Naturecan's Digest Capsules
In the same way a metropolis might implement an innovative infrastructure upgrade to improve its operations, Naturecan’s Digest Capsules have been crafted to bolster your gut health. These specially formulated capsules provide an easy and efficient method for enhancing the gut microbiome on your journey toward better digestive wellness.
Key benefits:
- 60 high-quality digest capsules
- 12 live bacterial cultures
- 10 Bio-Colony Forming Units
- LactoSpore® - a clinically validated probiotic
- Includes Chloride to support normal digestion (1)
- Synergetic formula
- Vegetarian friendly

14. Consulting a Healthcare Professional
In the same way that an urban planner seeks guidance from a specialist to shape city infrastructure, it’s wise to seek counsel from a healthcare expert for individualised recommendations regarding gut health.
They are equipped to offer tailored suggestions about incorporating prebiotics and probiotics into your regimen while taking into account your unique health requirements and any possible digestive distress you might experience prior to consuming these supplements.
15. Antibiotics: Use with Caution
Like a thriving metropolis carefully managing its vital resources, the prudent use of antibiotics is essential for safeguarding your gut microbiome. The indiscriminate use of these medications can diminish the diversity of microbes in your digestive system, wiping out advantageous organisms and resulting in adverse health effects. It’s important to resort to antibiotic treatments only when they’re truly needed. Always seek advice from a healthcare expert who can provide guidance on their appropriate use.
16. Cutting Back on Red Meat
Similar to how a city would reduce pollution for the better health of its citizens, reducing your consumption of red meat can foster a healthier gut microbiome. Lowering the amount of red meat you eat can result in adjustments within your gut flora, including diminishing microbes associated with illness and boosting those that are advantageous.
Table summary
Having delved into the 16 measures to enhance your gut microbiome, we should encapsulate them in a succinct table for easy reference. This at-a-glance tool offers you an array of strategies to fortify and improve your gut health.
| Method | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Food Variety | Consuming a wide range of foods can lead to a diverse microbiome, which is beneficial for gut health. Diversity in diet introduces a variety of nutrients that support different microbial species. |
| Legumes | Legumes are high in fibre, which is not digested by the body but is beneficial for the gut bacteria. This can help improve the growth of healthy bacteria. |
| Eat More Fruit and Veg | Fruits and vegetables are rich in fiber and other nutrients that are beneficial for gut bacteria. They can help increase the diversity and number of beneficial bacteria. |
| Choose Whole Grains | Wholegrains contain high amounts of fiber and non-digestible carbohydrates that bacteria ferment to produce short-chain fatty acids, beneficial for gut health. |
| Drink Coffee | Coffee is rich in polyphenols, which are metabolized by gut bacteria and may promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. |
| Eat Nuts and Seeds | Nuts and seeds are another good source of fibre, vitamins, and minerals that can support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. |
| Fermented Foods | Fermented foods like yoghurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi contain probiotics, which are live bacteria beneficial for the gut microbiome. |
| Reducing Sugar and Processed Food | High intake of sugar and processed foods can harm the gut microbiome by promoting the growth of unhealthy bacteria. Reducing their intake can support gut health. |
| Improve Your Sleep | Quality sleep is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Disruptions in sleep patterns can negatively affect gut health. |
| Exercise | Regular physical activity can help enhance the diversity of the gut microbiome, potentially improving gut health and overall well-being. |
| Managing Stress | High levels of stress can negatively impact the gut microbiome. Stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can be beneficial. |
| Hydrate | Drinking plenty of water is beneficial for the mucosal lining of the intestines and can help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria. |
| Mindful Eating Habits | Eating slowly and being mindful of the body’s hunger and fullness signals can prevent overeating and support digestion, potentially benefiting gut health. |
| Prebiotics and Probiotics Supplements | Prebiotics provide food for beneficial bacteria, while probiotics are live beneficial bacteria. Supplements may help improve the balance of gut microbiota. Consulting healthcare professionals before starting is advisable. |
| Consulting Healthcare Professionals | Before making significant changes to diet or lifestyle, especially when introducing supplements, it’s important to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure these changes are suitable for your individual health needs. |
| Antibiotics and Cutting Back on Red Meats | Antibiotics can disrupt the gut microbiome. Use them only when necessary and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Reducing red meat intake may also benefit gut health by decreasing certain harmful bacteria. |
Creating a Personalized Gut Health Plan
Much like a unique blueprint is required for the prosperity of a metropolis, your gut demands an equally specialised strategy for optimal health. The initiation of such a tailored plan for gut health necessitates an in-depth analysis of one’s dietary habits, symptomatic expressions related to health, and elements tied to personal lifestyle. A bespoke plan geared towards nurturing gut wellness encompasses:
- Meal schedules that are both regular and diverse
- Practical aids including grocery lists, culinary blueprints (recipes), and advice on serving sizes
- Tactics designed to maintain equilibrium within the gut microbiome
- Guidance formulated to ensure the eating plan is feasible
It’s vital to regularly consult with a nutrition expert who can fine-tune your eating regimen by addressing any arising obstacles and making precise adjustments as needed. Given that each individual’s digestive system presents its own set of characteristics, approaches effective for some may not suit others. It’s important you invest time in getting acquainted with your specific gastrointestinal needs while teaming up with medical professionals. Together you can develop a protocol finely suited just for your system.
Takeaway message
In summary, enhancing the health of your gut microbiome necessitates a comprehensive strategy that involves altering your diet, modifying lifestyle habits, and seeking tailored advice from medical experts. This is not a matter of instantaneous solutions. It’s about sustaining dedication over time.
Make the decision to boost the wellbeing of your gut today. Keep in mind that maintaining a healthy gut lays down the essential groundwork for overall physical and mental wellness!
Summary
Navigating the vibrant metropolis that is your gut, we’ve underscored how vital gut health and grasping the nuances of the gut microbiome are to your overall well-being.
Our deep dive into 16 natural strategies for enhancing your gut microbiome ranged from diversifying what you eat and cutting back on processed foods to controlling stress levels and ensuring adequate sleep.
We emphasised seeking advice from a medical expert and formulating a tailored plan for maintaining good digestive health.
In summary, nurturing a robust, varied population of microbes in your digestive system is crucial to sustaining overall health, allowing you with proper measures to bolster it and thereby improve your general vitality.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to improve gut health?
To enhance gut health, one should focus on a diet rich in fibre and include a wide variety of foods. It’s important to minimise the intake of ultra-processed foods while ensuring ample hydration through water consumption. Incorporating polyphenol-rich foods into your lifestyle and diet changes, taking time to eat mindfully and slowly, as well as adding fermented food items, can all contribute towards maintaining a healthy gut.
Adopting these dietary practices supports the promotion of good digestive health.
How long does it take to fix gut microbiome?
For the majority of individuals, the gut microbiome typically reverts to its original state within a period ranging from one month to two months, although certain people might undergo extended periods before their recovery is complete.
Alterations in the human gut microbiome can commence in just a matter of days. It might take multiple years for the enduring advantages of these changes to be fully realised.
What foods improve your gut microbiome?
Consuming foods rich in prebiotics like bananas, whole grains, onions, greens, and garlic along with probiotic-rich items such as yoghurt can enhance your gut microbiome.
Adding these nutritional elements to what you eat may lead to a healthier gut.
Why is gut health important?
Maintaining a healthy gut is essential as it has a profound impact on overall physical and mental health. It is crucial for effective digestion, the absorption of nutrients, supports immune system efficacy, contributes to brain health, and can affect one’s susceptibility to various diseases such as gastrointestinal issues, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and some mental health conditions.
What are prebiotics and probiotics, and how do they help gut health?
Compounds known as prebiotics promote the proliferation of advantageous gut bacteria, whereas probiotics consist of live microorganisms and yeasts that contribute positively to your gut. These elements assist in maintaining equilibrium within your gut microbiome and enhance overall gut health.
References:
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26965756/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32233323/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34505614/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25267244/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35406140/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34642755/







